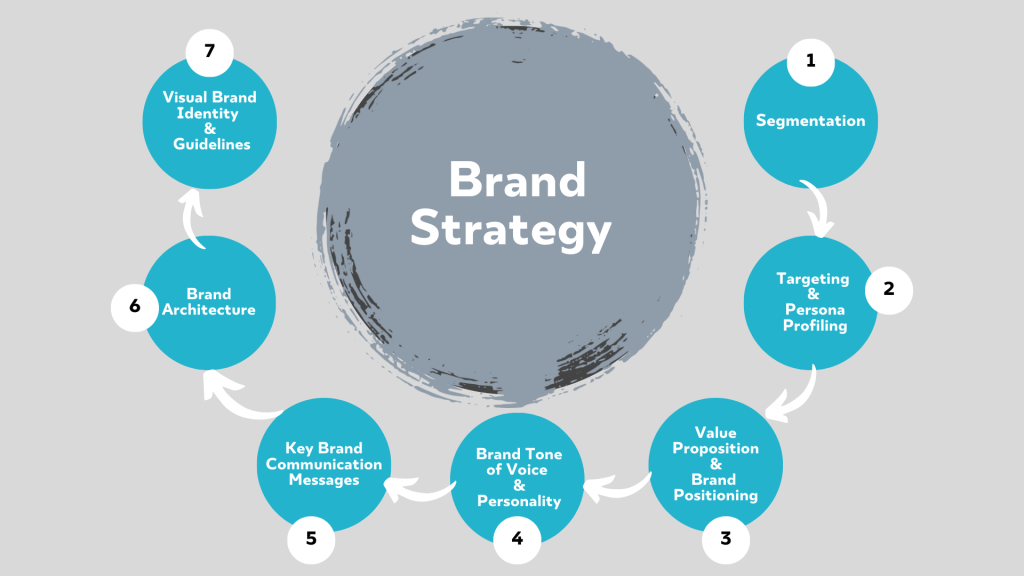
A Step By Step Guide For Building a Great Consumer Brand

Step 1
Identify your target Segment
Since no brand is able to deliver everything to everyone, the starting point is to segment the market and define your brand’s target consumer segment and profile based on different elements including demographics, psychographics, and lifestyle.
Example of a Target Consumer Profile for an upper mainstream home appliances brand may look like:
oMales & Females belonging to the B Socio Economic Class with a total household income in the range of EGP 25,000 – 40,000 monthly.
oThe male’s age is 30-40 years, while the female age is 25 – 35 years.
oThey attended private or public universities, and work in middle management at multinational companies, large local companies, banks, and high ranking government institutions.
oThey are engaged or newlyweds and eager to move to their new apartments at Fifth Settlement, 6th of October, Zayed, Sherouk, Obour, or Nasr City.
oThey are ambitious, eager to start a new life, excited and hopeful of the future.
oThey want to improve on the way things were done by their parents and are positively influenced by the world, the Internet, and Social Media.
oThey aspire to upgrade their lifestyles and reflect success and status.
oThey are health conscious and increasingly getting into sports.
oThey are price conscious and seek value for money purchases.
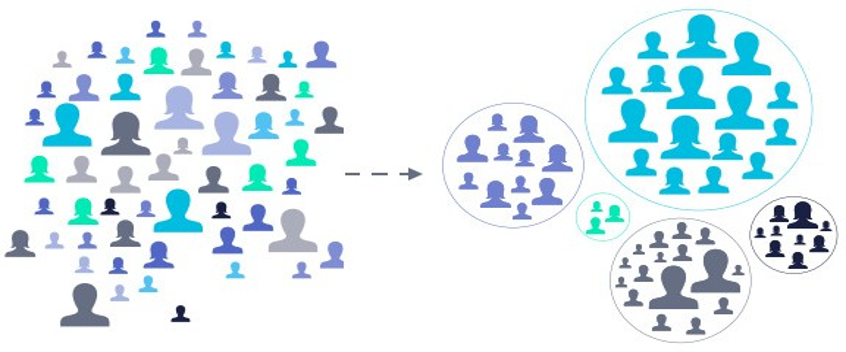
Step 2
Understand your consumer’s perceptions and needs
Research is necessary to understand the target consumer’s perceptions, functional, and emotional needs, mindset and to generate consumer in- sights.
Example of perceptions and needs of a target patient for an Eye Hospital may be:
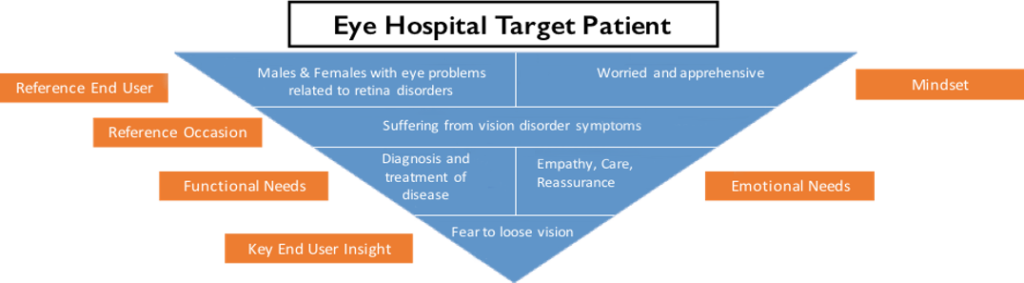
Step 3
Define the Brand Benefits
All brand components and elements of the marketing mix eventually must translate into clear consumer benefits. Developing a brand character, values, and brand essence are the essential elements to become relevant, convincing, and loved by your target consumer group.
Example of Brand Benefits of a high end Real Estate Developer Brand may look like:
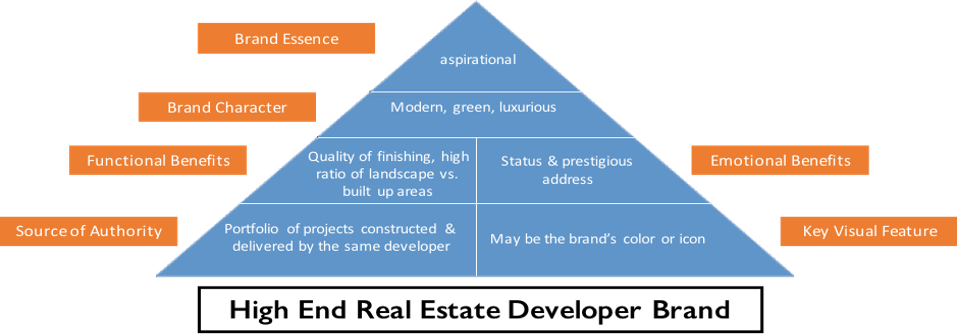
Step 4
Develop the Brand Promise
Once target consumer perceptions and needs are defined along with the brand’s benefits, character, essence, and unique selling point the brand promise is derived to represent the point where both ends of the pyramid model meet.
Examples of brand promises include:

“Bringing inspiration and innovation to every athlete”

“Simple, easy enjoyment with great service, cleanliness, and value”

“To inspire moments of optimism and uplift”
Step 5
Conduct a Competition Analysis
The developed brand proposition must be validated against competition offerings. Competition analysis must answer questions such as “where is my brand offering different from competition?”, “why should consumers choose my brand over competition?”

Step 6
Define Positioning
Positioning lies at the core of marketing strategy. It is the definition of how a brand wishes to be perceived by consumers. The goal is to create a unique impression on the consumer’s mind, so that the consumer associates the brand with something specific and desirable that is distinct from the market place.
Examples of different positioning charts within different FMCG sectors include the below:

Step 7
Brand Architecture
Brand architecture defines the relationship between the brand with the rest of portfolio and parent corporate brand. The most common brand architecture strategies are illustrated below with examples:
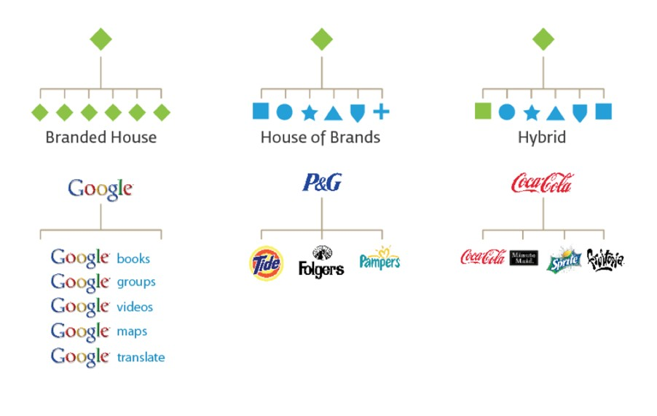
Step 8
Create the Brand’s Visual Representation
Design work should not be judged according to subjective individual likes and dislikes of team members. The purpose of design and creativity is to translate the brand’s essence into memorable visual representations, since such representations are far more effective in capturing the attention of consumer minds. Likewise, consumer minds are not able to differentiate between packaging and the actual product inside it. Hence, the importance of utilizing visual elements in establishing the required positioning.

Step 9
Define Communication Strategy, and tone of voice
The only objective of brand communication is to deliver on the marketing objectives. Marketing teams are required to set clear defined objectives, the strategy planning framework, and the brand’s tone of voice while briefing their creative counter parts. Creative teams are responsible to translate the communication brief into engaging, effective branded consumer messages revolving around key insights, while capturing the brand’s essence, positioning, and the world’s “Zeitgeist”.

Step 10
Integrate the Brand Essence into every aspect of the business
Effective branding cannot work in isolation from the actual product offering and rest of business aspects such as product development, customer service and sales. Consumers believe brands, when the brand values and promise is reflected across every touchpoint.

Example of a brand whose essence and promise are reflected in all consumer’s touchpoints include:
Apple’s brand promise revolves around innovation and thinking differently. It is not only reflected in their products and communication, but also across every other customer touchpoint. Apple stores with their intriguing interior design, and innovative customer experience, have disrupted the concept of shopping and stores for all retailers.
about the author

Nader Elhamy
A senior marketing, commercial management & Digital Strategist with over 20 years’ experience.
Founder & Managing Partner of Toolbox Marketing Consulting.
Member of the commercial management team, which conducted the turnaround of Al-Ahram Beverages Company.
He has launched, re-launched and managed some of Egypt’s largest and most successful brands across a variety of sectors including FMCG, Real Estate, Destinations, Food & Beverages, Hospitality, Textiles, Retail, Media, White Goods, Electrical Accessories, and Manufacturing.